2024
ERK hyperactivation in epidermal keratinocytes impairs intercellular adhesion and drives Grover disease pathology
Simpson CL, Tiwaa A, Zaver SA, Johnson CJ, Chu EY, Harms PW, Gudjonsson JE. JCI Insight. 2024 Nov 8;9(21):e182983. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.182983. PMID: 39325541
Abstract and Highlights
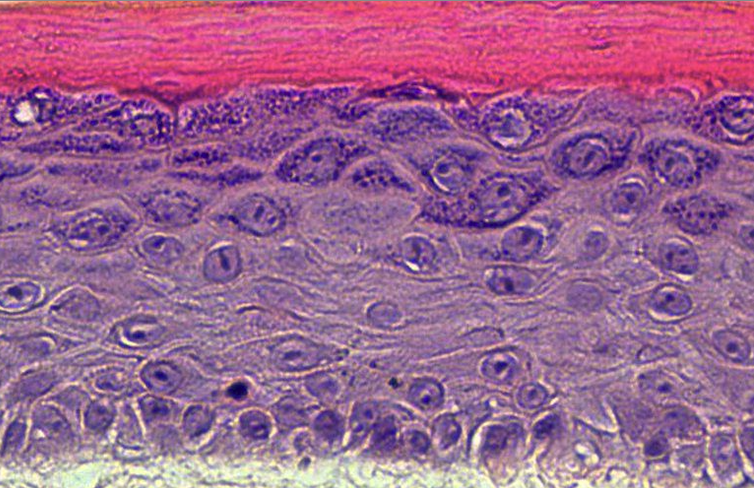
- Grover disease is an acquired epidermal blistering disorder in which keratinocytes lose intercellular connections. While its pathologic features are well defined, its etiology remains unclear, and there is no FDA-approved therapy. Interestingly, Grover disease was a common adverse event in clinical trials for cancer using B-RAF inhibitors, but it remained unknown how B-RAF blockade compromised skin integrity. Here, we identified ERK hyperactivation as a key driver of Grover disease pathology. We leveraged a fluorescent biosensor to confirm that the B-RAF inhibitors dabrafenib and vemurafenib paradoxically activated ERK in human keratinocytes and organotypic epidermis, disrupting cell-cell junctions and weakening epithelial integrity. Consistent with clinical data showing that concomitant MEK blockade prevents Grover disease in patients receiving B-RAF inhibitors, we found that MEK inhibition suppressed ERK and rescued cohesion of B-RAF-inhibited keratinocytes. Validating these results, we demonstrated ERK hyperactivation in patient biopsies from vemurafenib-induced Grover disease and from spontaneous Grover disease, revealing a common etiology for both. Finally, in line with our recent identification of ERK hyperactivation in Darier disease, a genetic disorder with identical pathology to Grover disease, our studies uncovered that the pathogenic mechanisms of these diseases converge on ERK signaling and support MEK inhibition as a therapeutic strategy.
Pumping the Breaks on Acantholytic Skin Disorders: Targeting Calcium Pumps, Desmosomes, and Downstream Signaling in Darier, Hailey-Hailey, and Grover Disease
Harmon RM, Ayers JL, McCarthy EF, Kowalczyk AP, Green KJ, Simpson CL. J Invest Dermatol. 2024 Aug 28:S0022-202X(24)01925-0. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2024.06.1289. PMID: 39207315
Abstract and Highlights
- Acantholytic skin disorders, by definition, compromise intercellular adhesion between epidermal keratinocytes. The root cause of blistering in these diseases traces back to direct disruption of adhesive cell-cell junctions, exemplified by autoantibody-mediated attack on desmosomes in pemphigus. However, genetic acantholytic disorders originate from more indirect mechanisms. Darier disease and Hailey-Hailey disease arise from mutations in the endoplasmic reticulum calcium pump, SERCA2, and the Golgi calcium/manganese pump, SPCA1, respectively. Though the disease-causing mutations have been known for nearly 25 years, the mechanistic linkage between dysregulation of intracellular ion stores and weakening of cell-cell junctions at the plasma membrane remains puzzling. The molecular underpinnings of a related idiopathic disorder, Grover disease, are even less understood. Due to an incomplete understanding of acantholytic pathology at the molecular level, these disorders lack proven, targeted treatment options, leaving patients with the significant physical and psychological burdens of chronic skin blistering, infections, and pain. This article aims to review what is known at the molecular, cellular, and clinical levels regarding these under-studied disorders and to highlight knowledge gaps and promising ongoing research. Armed with this knowledge, our goal is to aid investigators in defining essential questions about disease pathogenesis and to accelerate progress toward novel therapeutic strategies.
Genetic Tools for Cell Lineage Tracing and Profiling Developmental Trajectories in the Skin
Nathans JF, Ayers JL, Shendure J, Simpson CL. J Invest Dermatol. 2024 May;144(5):936-949. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2024.02.006.. PMID: 38643988
Abstract and Highlights
- The epidermis is the body’s first line of protection against dehydration and pathogens, continually regenerating the outermost protective skin layers throughout life. During both embryonic development and wound healing, epidermal stem and progenitor cells must respond to external stimuli and insults to build, maintain, and repair the cutaneous barrier. Recent advances in CRISPR-based methods for cell lineage tracing have remarkably expanded the potential for experiments that track stem and progenitor cell proliferation and differentiation over the course of tissue and even organismal development. Additional tools for DNA-based recording of cellular signaling cues promise to deepen our understanding of the mechanisms driving normal skin morphogenesis and response to stressors as well as the dysregulation of cell proliferation and differentiation in skin diseases and cancer. In this review, we highlight cutting-edge methods for cell lineage tracing, including in organoids and model organisms, and explore how cutaneous biology researchers might leverage these techniques to elucidate the developmental programs that support the regenerative capacity and plasticity of the skin.
2023
Exacerbation of Darier disease with lithium therapy
Tamazian S, Simpson CL. Dermatol Online J. 2023 Oct 15;29(5). doi: 10.5070/D329562405.. PMID: 38478641
Abstract and Highlights
- Darier disease is an autosomal dominant blistering disorder linked to mutation of the endoplasmic reticulum calcium pump, SERCA2, which compromises keratinocyte adhesion and differentiation. Beyond the typical keratotic and eroded skin lesions, patients with Darier disease often present with psychiatric co-morbidities. Herein, we present a biopsy-confirmed case of Darier disease in a patient with bipolar disorder, whose cutaneous disease dramatically worsened upon initiation of lithium therapy. In consultation with the patient’s psychiatrist, lithium was tapered, leading to rapid improvement in her skin. This case highlights the potential for lithium to complicate management of Darier disease and underscores the need for dermatologists to collaborate with psychiatrists to optimize both cutaneous and mental health in patients.
Targeting SERCA2 in organotypic epidermis reveals MEK inhibition as a therapeutic strategy for Darier disease
Zaver SA, Sarkar MK, Egolf S, Zou J, Tiwaa A, Capell BC, Gudjonsson JE, Simpson CL. JCI Insight. 2023;8(18):e170739. Published 2023 Sep 22. doi:10.1172/jci.insight.170739. PMID: 37561594
Abstract and Highlights
- Mutation of the ATP2A2 gene encoding sarco-endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase 2 (SERCA2) was linked to Darier disease more than 2 decades ago; however, there remain no targeted therapies for this disorder causing recurrent skin blistering and infections. Since Atp2a2-knockout mice do not phenocopy its pathology, we established a human tissue model of Darier disease to elucidate its pathogenesis and identify potential therapies. Leveraging CRISPR/Cas9, we generated human keratinocytes lacking SERCA2, which replicated features of Darier disease, including weakened intercellular adhesion and defective differentiation in organotypic epidermis. To identify pathogenic drivers downstream of SERCA2 depletion, we performed RNA sequencing and proteomics analysis. SERCA2-deficient keratinocytes lacked desmosomal and cytoskeletal proteins required for epidermal integrity and exhibited excess MAPK signaling, which modulates keratinocyte adhesion and differentiation. Immunostaining patient biopsies substantiated these findings, with lesions showing keratin deficiency, cadherin mislocalization, and ERK hyperphosphorylation. Dampening ERK activity with MEK inhibitors rescued adhesive protein expression and restored keratinocyte sheet integrity despite SERCA2 depletion or chemical inhibition. In sum, coupling multiomic analysis with human organotypic epidermis as a preclinical model, we found that SERCA2 haploinsufficiency disrupts critical adhesive components in keratinocytes via ERK signaling and identified MEK inhibition as a treatment strategy for Darier disease.
Live Imaging with Genetically Encoded Physiologic Sensors and Optogenetic Tools
Zaver SA, Johnson CJ, Berndt A, Simpson CL. J Invest Dermatol. 2023 Mar;143(3):353-361.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2022.12.002. PMID: 36822769
Abstract and Highlights
- Barrier tissues such as the epidermis employ complex signal transduction systems to execute morphogenetic programs and to rapidly respond to environmental cues to promote homeostasis. Recent advances in live-imaging techniques and tools allow precise spatial and temporal monitoring and manipulation of intracellular signaling cascades. Leveraging the chemistry of naturally occurring light-sensitive proteins, genetically encoded fluorescent biosensors have emerged as robust tools for visualizing dynamic signaling events. In contrast, optogenetic protein constructs permit laser-mediated control of signal receptors and effectors within live cells, organoids, and even model organisms. In this paper, we review the basic principles underlying novel biosensors and optogenetic tools and highlight how recent studies in cutaneous biology have leveraged these imaging strategies to illuminate the spatiotemporal signals regulating epidermal development, barrier formation, and tissue homeostasis.
2021
NIX initiates mitochondrial fragmentation via DRP1 to drive epidermal differentiation
Simpson CL, Tokito MK, Uppala R, Sarkar MK, Gudjonsson JE, Holzbaur EL. Cell Reports. Feb 2; 34(5): 108689. DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.108689. PMID: 33535046
Abstract and Highlights
- The epidermis regenerates continually to maintain a protective barrier at the body’s surface composed of differentiating keratinocytes. Maturation of this stratified tissue requires that keratinocytes undergo wholesale organelle degradation upon reaching the outermost tissue layers to form compacted, anucleate cells. Through live imaging of organotypic cultures of human epidermis, we find that regulated breakdown of mitochondria is critical for epidermal development. Keratinocytes in the upper layers initiate mitochondrial fragmentation, depolarization, and acidification upon upregulating the mitochondrion-tethered autophagy receptor NIX. Depleting NIX compromises epidermal maturation and impairs mitochondrial elimination, whereas ectopic NIX expression accelerates keratinocyte differentiation and induces premature mitochondrial fragmentation via the guanosine triphosphatase (GTPase) DRP1. We further demonstrate that inhibiting DRP1 blocks NIX-mediated mitochondrial breakdown and disrupts epidermal development. Our findings establish mitochondrial degradation as a key step in terminal keratinocyte differentiation and define a pathway operating via the mitophagy receptor NIX in concert with DRP1 to drive epidermal morphogenesis.
Expanding Armor-Like Scales in a Middle-Aged Woman: Pemphigus vulgaris.
Bax CE, Smith RJ, Simpson CL. SKIN: The Journal of Cutaneous Medicine, 5(1), 78–79.
Abstract and Highlights
- A woman in her 50s presented with a 7-month history of worsening pruritic papules and bullae on her face, trunk, arms, and axillae. Her medical history was significant for Meniere disease and hyperthyroidism. At an outside clinic, an initial skin biopsy from the arm showed intraepidermal acantholysis with dyskeratosis and she was diagnosed with transient acantholytic dermatosis (Grover disease). Treatments included triamcinolone ointment, doxycycline, antihistamines, and short courses of prednisone without clinical improvement. Over the following two months, her eruption worsened, and she developed painful oral mucosal erosions. Physical examination revealed vegetative scale-crusts overlying erosions on the face, arms, and chest in an armor-like pattern as well as flaccid bullae on the back and erosions of the gingival and labial mucosae. A shave biopsy of the skin from the upper back was performed. Direct immunofluorescence showed intercellular epidermal deposition of IgG and C3. Indirect immunofluorescence was positive on monkey esophagus substrate in an intercellular pattern at a titer of 1:5120 and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) quantified anti-desmoglein-1 (Dsg1) and anti-desmoglein-3 (Dsg3) antibodies at 620 (negative<20) and 176 units (negative<20), respectively.
MLL4 mediates differentiation and tumor suppression through ferroptosis
Egolf S, Zou J, Anderson A, Simpson CL, Aubert Y, Ge K, Seykora JT, Capell BC. Science Advances, 7(50):eabj9141. DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abj9141. PMID: 34890228
Abstract and Highlights
- The epigenetic regulator, MLL4 (KMT2D), has been described as an essential gene in both humans and mice. In addition, it is one of the most commonly mutated genes in all of cancer biology. Here, we identify a critical role for Mll4 in the promotion of epidermal differentiation and ferroptosis, a key mechanism of tumor suppression. Mice lacking epidermal Mll4, but not the related enzyme Mll3 (Kmt2c), display features of impaired differentiation and human precancerous neoplasms, all of which progress with age. Mll4 deficiency profoundly alters epidermal gene expression and uniquely rewires the expression of key genes and markers of ferroptosis (Alox12, Alox12b, and Aloxe3). Beyond revealing a new mechanistic basis for Mll4-mediated tumor suppression, our data uncover a potentially much broader and general role for ferroptosis in the process of differentiation and skin homeostasis.
Pruritic Rash and Oral Erosions During Nivolumab Treatment for Melanoma: Bullous pemphigoid
Tamazian S, Chu EY, Simpson CL. SKIN: The Journal of Cutaneous Medicine, 5(1), 80–82.
Abstract and Highlights
- A 76-year-old man with a history of stage 3 melanoma treated with nivolumab presented with a persistent eruption of intensely pruritic papules on the trunk that started six months after initiating immunotherapy. He denied skin blistering. The patient also reported recurrent blood-filled blisters in the mouth that ruptured to form painful erosions. Physical examination revealed scattered erythematous papules without vesiculation on the back (Figure 1A), excoriated papules on the chest (Figure 1B), and several shallow erosions of the buccal mucosa (Figure 1C). Immunohistochemical (IHC) staining of the skin biopsy showed linear deposition of complement protein C3d along the dermal-epidermal junction (Figure 2) and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) revealed anti-BP180 antibodies, confirming a diagnosis of bullous pemphigoid
Actin cables and comet tails organize mitochondrial networks in mitosis.
Moore AS, Coscia SM, Simpson CL, Ortega FE, Wait EC, Heddleston JM, Nirschl JJ, Obara CJ, Guedes-Dias P, Boecker CA, Chew T-L, Theriot JA, Lippincott-Schwartz J, Holzbaur EL. Nature. 2021 Mar; 591(7851): 659-664. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-021-03309-5. PMID: 33658713
Abstract and Highlights
- Symmetric cell division requires the even partitioning of genetic information and cytoplasmic contents between daughter cells. Whereas the mechanisms coordinating the segregation of the genome are well known, the processes that ensure organelle segregation between daughter cells remain less well understood1. Here we identify multiple actin assemblies with distinct but complementary roles in mitochondrial organization and inheritance in mitosis. First, we find a dense meshwork of subcortical actin cables assembled throughout the mitotic cytoplasm. This network scaffolds the endoplasmic reticulum and organizes three-dimensional mitochondrial positioning to ensure the equal segregation of mitochondrial mass at cytokinesis. Second, we identify a dynamic wave of actin filaments reversibly assembling on the surface of mitochondria during mitosis. Mitochondria sampled by this wave are enveloped within actin clouds that can spontaneously break symmetry to form elongated comet tails. Mitochondrial comet tails promote randomly directed bursts of movement that shuffle mitochondrial position within the mother cell to randomize inheritance of healthy and damaged mitochondria between daughter cells. Thus, parallel mechanisms mediated by the actin cytoskeleton ensure both equal and random inheritance of mitochondria in symmetrically dividing cells.
2020
Autoimmune bullous disease in skin of color: A case series
Tamazian S, Simpson CL. JAAD Case Rep, 2020. 6(11):1173-8. DOI: 10.1016/j.jdcr.2020.08.035. PMID: 33145386
Abstract and Highlights
- Medical education must prepare clinicians to care for diverse populations, which is especially important in dermatology, as cutaneous disorders present differently depending on skin pigmentation. Patients with nonwhite skin tones are underrepresented in the dermatologic literature and broader educational resources, a deficiency that is particularly problematic for rare disorders like autoimmune bullous diseases (AIBD). We present a case series of AIBD in patients with nonwhite skin tones, emphasizing differences in disease presentation and pigmentary sequelae.
Teledermatology consultation can optimize treatment of cutaneous disease by non-dermatologists in under-resourced clinics.
Holmes AN, Chansky PB, Simpson CL. Telemedicine & e-Health, 26(10):1284-90. DOI: 10.1089/tmj.2019.0217. PMID: 31800370
Abstract and Highlights
- Background: Access to dermatologists is limited for disadvantaged patients, who may receive suboptimal dermatologic care from nonspecialists. We assessed if teledermatology could improve primary care provider (PCP)-delivered care for cutaneous disease at a clinic serving uninsured patients.
- Materials and Methods: Utilizing the American Academy of Dermatology’s free AccessDerm program, we offered store-and-forward teledermatology to PCPs, who initiated consultations at will during clinical care independent of the study. We retrospectively analyzed all consultations from 2013 to 2017 and collected patient age/sex, teledermatologist diagnosis, time to teledermatologist reply, time to next dermatology appointment, as well as PCP- and teledermatologist-proposed care plans.
- Results: Retrospective analysis of 131 consults revealed a 37-h mean teledermatology response-time versus a 14-day appointment wait (p < 0.00001). Teledermatologists provided a definitive care plan without in-person evaluation for 82 (65%) of completed consults and recommended interim treatments while awaiting appointments in 15 cases, thus accelerating care plan delivery in 97 cases (76%). The triage decision rate differed among diagnostic categories; deferral to in-person evaluation was more frequent for neoplasms (p < 0.0001). When PCPs specified preconsult treatment plans, 82% differed from teledermatologist-advised management. Following teledermatologist recommendations would have changed the clinical course in 70% of cases, potentially avoiding suboptimal care, including inappropriate corticosteroids, antimicrobials, and emergency room referrals.
- Conclusions: We found teledermatology can effectively guide PCPs in resource-limited settings by accelerating delivery of dermatologist-recommended care plans for uninsured patients. Expanding teledermatology for PCPs in under-resourced clinics has the potential to improve treatment of cutaneous disease by nonspecialists and to mitigate suboptimal care for disadvantaged patients.
Comparison of C3d immunohistochemical staining to ELISA and immunofluorescence for diagnosis of bullous pemphigoid.
Wang LL, Moshiri AS, Novoa R, Simpson CL, Takeshita J, Payne AS, Chu EY. J Amer Acad of Dermatol, 2020. 83(1):172-8. DOI: 10.1016/j.jaad.2020.02.020. PMID: 32068042
Abstract and Highlights
- Background: Bullous pemphigoid (BP), the most common autoimmune blistering disease, may be diagnostically challenging. Direct immunofluorescence (DIF), indirect immunofluorescence (IIF), enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), and recently, C3d immunohistochemistry (IHC), are used as adjuncts to diagnosis.
- Objective: To compare C3d IHC to DIF, IIF, and ELISA testing in BP diagnosis.
- Methods: C3d IHC was performed on skin biopsy specimens from 51 patients (27 with BP and 24 with other blistering diseases) and compared to DIF and IIF, with anti-BP180 or anti-BP230 ELISA results used as the gold standard.
- Results: We found C3d IHC, DIF, and IIF had similar sensitivity (74.1%, 63.1%, and 70.4%), specificity (95.8%, 100%, and 100%), positive predictive value (95.2%, 100%, and 100%), and negative predictive value (76.7%, 70.6%, and 75%) for BP. Cases with positive C3d IHC, DIF, and IIF had significantly higher anti-BP180 and anti-BP230 by ELISA than cases with negative testing (P < .0001). False-negative IIF results were associated with lower BP230 compared with true-positive results (P = .03).
- Limitations: This was a single-center, retrospective study.
- Conclusion: Our study compared C3d IHC to DIF and IIF in BP diagnosis, demonstrating C3d IHC on fixed tissue provides similar diagnostic utility to immunofluorescence and ELISA.
- Keywords: C3d immunohistochemistry; ELISA; bullous pemphigoid; diagnosis; direct immunofluorescence; indirect immunofluorescence.
2019
LSD1 inhibition promotes epithelial differentiation through de-repression of fate-determining transcription factors.
Egolf S, Aubert Y, Doepner M, Maldonado-Lopez A, Anderson A, Lan Y, Simpson CL, Ridky TW, Capell BC. Cell Reports, 28(8):1981-92. DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.07.058. PMID: 31433976
Abstract and Highlights
- Self-renewing somatic tissues depend upon the proper balance of chromatin-modifying enzymes to coordinate progenitor cell maintenance and differentiation, disruption of which can promote carcinogenesis. As a result, drugs targeting the epigenome hold significant therapeutic potential. The histone demethylase, LSD1 (KDM1A), is overexpressed in numerous cancers, including epithelial cancers; however, its role in the skin is virtually unknown. Here we show that LSD1 directly represses master epithelial transcription factors that promote differentiation. LSD1 inhibitors block both LSD1 binding to chromatin and its catalytic activity, driving significant increases in H3K4 methylation and gene transcription of these fate-determining transcription factors. This leads to both premature epidermal differentiation and the repression of squamous cell carcinoma. Together these data highlight both LSD1’s role in maintaining the epidermal progenitor state and the potential of LSD1 inhibitors for the treatment of keratinocyte cancers, which collectively outnumber all other cancers combined.
2018
Enlarging red papulonodule on the chest: Renal cell carcinoma.
Shaigany S, Simpson CL, Micheletti R. Cutis, 101(2):78, 117-8. PMID: 29554160
Abstract and Highlights
- A man in his 60s presented with a subcutaneous nodule on the right side of the chest. Due to impaired mental status, he was unable to describe the precise age of the lesion, but his wife reported it had been present at least several weeks. She recently noted a new, bright red growth on top of the nodule. The lesion was asymptomatic but seemed to be growing in size. Physical examination revealed a 3-cm firm fixed nodule on the right side of the chest with an overlying, exophytic bright red papule. No similar lesions were found elsewhere on physical examination. A punch biopsy of the lesion was performed.
KMT2D regulates p63 target enhancers to coordinate epithelial homeostasis
Lin-Shiao E, Lan Y, Coradin M, Anderson A, Donahue G, Simpson CL, Sen P, Saffie R, Busino L, Garcia BA, Berger SL, Capell BC. Genes and Development, 32(2):181-93. DOI: 10.1101/gad.306241.117. PMID: 29440247
Abstract and Highlights
- Epithelial tissues rely on a highly coordinated balance between self-renewal, proliferation, and differentiation, disruption of which may drive carcinogenesis. The epigenetic regulator KMT2D (MLL4) is one of the most frequently mutated genes in all cancers, particularly epithelial cancers, yet its normal function in these tissues is unknown. Here, we identify a novel role for KMT2D in coordinating this fine balance, as depletion of KMT2D from undifferentiated epidermal keratinocytes results in reduced proliferation, premature spurious activation of terminal differentiation genes, and disorganized epidermal stratification. Genome-wide, KMT2D interacts with p63 and is enriched at its target enhancers. Depletion of KMT2D results in a broad loss of enhancer histone modifications H3 Lys 4 (H3K4) monomethylation (H3K4me1) and H3K27 acetylation (H3K27ac) as well as reduced expression of p63 target genes, including key genes involved in epithelial development and adhesion. Together, these results reveal a critical role for KMT2D in the control of epithelial enhancers and p63 target gene expression, including the requirement of KMT2D for the maintenance of epithelial progenitor gene expression and the coordination of proper terminal differentiation.
Teledermatology leading to an important diagnosis in an underserved clinic.
Da Silva DM, Roth RR, Simpson CL. Dermatology Online Journal, 24(4):8. PMID: 29906004
Abstract and Highlights
- Cutaneous signs can be the first manifestation of important medical diagnoses, including inherited cancer syndromes, but access to dermatologic evaluation is especially challenging for uninsured patients. Herein, we present a case in which a volunteer academic teledermatology triage program was used by a community health clinic to make a diagnosis of multiple cutaneous leiomyomas, which confer a high likelihood of hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell cancer syndrome, also known as Reed syndrome; this prompted malignancy screening for the patient. Importantly, this case underscores the potential for teledermatology to improve access to dermatologist evaluation and make crucial diagnoses in patients with barriers to care.
2017
Implementation of a dermatology teletriage system to improve access in an underserved clinic: A retrospective study
Chansky PB, Simpson CL, Lipoff JB. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 77(5):975-7. DOI: 10.1016/j.jaad.2017.06.025. PMID: 29029909
2016
Refractory cutaneous alternariosis successfully treated with Mohs surgery and full-thickness skin grafting.
Simpson CL, Craig-Muller S, Sobanko JF, Weikert BC, Micheletti RG. Dermatologic Surgery, 42(3):426-9. DOI: 10.1097/DSS.0000000000000625. PMID: 26945322
Dynamic actin cycling through mitochondrial subpopulations locally regulates the fission-fusion balance within mitochondrial networks.
Moore AS, Wong YC, Simpson CL, Holzbaur EL. Nature Communications, 7:12886. DOI: 10.1038/ncomms12886. PMID: 27686185
Abstract and Highlights
- Mitochondria form interconnected networks that dynamically remodel in response to cellular needs. Using live-cell imaging, we investigate the role of the actin cytoskeleton in regulating mitochondrial fission and fusion. We identify cycling of actin filaments onto and off of subsets of cellular mitochondria. The association of actin filaments with mitochondrial subpopulations is transient; actin quickly disassembles, then reassembles around a distinct subpopulation, efficiently cycling through all cellular mitochondria within 14 min. The focal assembly of actin induces local, Drp1-dependent fragmentation of the mitochondrial network. On actin disassembly, fragmented mitochondria undergo rapid fusion, leading to regional recovery of the tubular mitochondrial network. Cycling requires dynamic actin polymerization and is blocked by inhibitors of both Arp2/3 and formins. We propose that cyclic assembly of actin onto mitochondria modulates the fission/fusion balance, promotes network remodelling and content mixing, and thus may serve as an essential mechanism regulating mitochondrial network homeostasis.
2015
Photo-distributed lichenoid eruption secondary to direct anti-viral therapy for hepatitis C.
Simpson CL, McCausland D, Chu EY. Journal of Cutaneous Pathology, 42(10):769-73. DOI: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2015.1359. PMID: 25974215
Abstract and Highlights
- Novel direct anti-viral agents are emerging as effective treatments for hepatitis C virus (HCV) and provide an alternative to the year-long standard therapy with interferon and ribavirin. However, cutaneous side effects from these new medications, including rash, pruritus and photosensitivity, are among the most commonly reported adverse events and have resulted in therapy discontinuation in some cases. Here, we report two cases of a photo-distributed lichenoid eruption that occurred within 1 month of starting anti-viral therapy with simeprevir and sofosbuvir without interferon or ribavirin. This report provides the first histologic description of the cutaneous eruption associated with direct anti-viral therapy for HCV and highlights the importance of recognizing and treating the often intolerable dermatologic side effects of these novel medications, the incidence of which is likely to increase as direct anti-viral agents may become the standard of care for HCV.
A Crusted Papule in a Premature Neonate.
Simpson CL, Boos MD, Castelo-Soccio L. JAMA Pediatrics, 169(12):1173-4. DOI: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2015.1359. PMID: 26642112
Abstract and Highlights
- A male neonate was born at 25 weeks’ gestation by cesarean delivery because of hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelet count (HELLP) syndrome in his primigravid mother, who also had systemic lupus erythematosus managed with hydroxychloroquine, aspirin, and prednisone during pregnancy. The patient’s premature birth was complicated by acute respiratory distress that necessitated intubation and necrotizing enterocolitis that required parenteral nutrition. At birth, the patient was found to be mildly anemic (hemoglobin level, 11.0 g/dL [to convert to grams per liter, multiply by 10]) and thrombocytopenic (platelet count, 120 × 103/µL [to convert to 109/L, multiply by 1]) with concomitant intraventricular hemorrhage. Although afebrile, he was treated empirically for sepsis with vancomycin hydrochloride and cefepime hydrochloride. A cerebrospinal fluid culture result was positive for Staphylococcus epidermidis, but the results of additional blood cultures were negative for organisms. On day 8 after birth, a 0.5-cm, circular, crusted papule with a surrounding rim of erythema on the left hip was noted. A punch biopsy of the lesion was performed.
Infant with a Unilateral Parotid Mass, Recurrent Otitis Media, and Macrocephaly: Plexiform Neurofibroma.
Boos MD, Simpson CL, Castelo-Soccio L. JAMA Pediatrics, 169(8):783-4. DOI: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2015.0900. PMID: 26237456
Abstract and Highlights
- A 9-month-old boy presented with a left-sided facial mass. His perinatal history was notable for macrosomia, macrocephaly, left-sided failure on newborn hearing screen, and a congenital hypertrichotic patch of the left scalp. During the first few months, he was observed to frequently tug at his left ear while displaying apparent discomfort and sleeping difficulties. He was treated empirically with multiple antibiotics for presumed otitis media and subsequently had bilateral myringotomy tubes placed. When the left side of his face became more swollen, magnetic resonance imaging was performed at 8 months of age and revealed a left-sided parotid mass. He was referred to our institution for further evaluation.
2013
Desmoglein-1/Erbin interaction suppresses ERK activation to support epidermal differentiation.
Harmon RM, Simpson CL, Johnson JL, Koetsier JL, Dubash AD, Najor NA, Sarig O, Sprecher E, Green KJ. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 123(4):1556-70. DOI: 10.1172/JCI65220. PMID: 23524970
Abstract and Highlights
- Genetic disorders of the Ras/MAPK pathway, termed RASopathies, produce numerous abnormalities, including cutaneous keratodermas. The desmosomal cadherin, desmoglein-1 (DSG1), promotes keratinocyte differentiation by attenuating MAPK/ERK signaling and is linked to striate palmoplantar keratoderma (SPPK). This raises the possibility that cutaneous defects associated with SPPK and RASopathies share certain molecular faults. To identify intermediates responsible for executing the inhibition of ERK by DSG1, we conducted a yeast 2-hybrid screen. The screen revealed that Erbin (also known as ERBB2IP), a known ERK regulator, binds DSG1. Erbin silencing disrupted keratinocyte differentiation in culture, mimicking aspects of DSG1 deficiency. Furthermore, ERK inhibition and the induction of differentiation markers by DSG1 required both Erbin and DSG1 domains that participate in binding Erbin. Erbin blocks ERK signaling by interacting with and disrupting Ras-Raf scaffolds mediated by SHOC2, a protein genetically linked to the RASopathy, Noonan-like syndrome with loose anagen hair (NS/LAH). DSG1 overexpression enhanced this inhibitory function, increasing Erbin-SHOC2 interactions and decreasing Ras-SHOC2 interactions. Conversely, analysis of epidermis from DSG1-deficient patients with SPPK demonstrated increased Ras-SHOC2 colocalization and decreased Erbin-SHOC2 colocalization, offering a possible explanation for the observed epidermal defects. These findings suggest a mechanism by which DSG1 and Erbin cooperate to repress MAPK signaling and promote keratinocyte differentiation.
2011
The calcium ATPase SERCA2 regulates desmoplakin dynamics and intercellular adhesive strength through modulation of PKCα signaling.
Hobbs RP, Amargo EV, Somasundaram A, Simpson CL, Prakriya M, Denning MF, Green KJ. FASEB Journal, 25(3):990-1001. DOI: 10.1096/fj.10-163261. PMID: 21156808
Abstract and Highlights
- Darier’s disease (DD) is an inherited autosomal-dominant skin disorder characterized histologically by loss of adhesion between keratinocytes. DD is typically caused by mutations in sarcoendoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+)-ATPase isoform 2 (SERCA2), a major regulator of intracellular Ca(2+) homeostasis in the skin. However, a defined role for SERCA2 in regulating intercellular adhesion remains poorly understood. We found that diminution of SERCA2 function by pharmacological inhibition or siRNA silencing in multiple human epidermal-derived cell lines was sufficient to disrupt desmosome assembly and weaken intercellular adhesive strength. Specifically, SERCA2-deficient cells exhibited up to a 60% reduction in border translocation of desmoplakin (DP), the desmosomal cytolinker protein necessary for intermediate filament (IF) anchorage to sites of robust cell-cell adhesion. In addition, loss of SERCA2 impaired the membrane translocation of protein kinase C α (PKCα), a known regulator of DP-IF association and desmosome assembly, to the plasma membrane by up to 70%. Exogenous activation of PKCα in SERCA2-deficient cells was sufficient to rescue the defective DP localization, desmosome assembly, and intercellular adhesive strength to levels comparable to controls. Our findings indicate that SERCA2-deficiency is sufficient to impede desmosome assembly and weaken intercellular adhesive strength via a PKCα-dependent mechanism, implicating SERCA2 as a novel regulator of PKCα signaling.
2010
Plakoglobin rescues adhesive defects induced by ectodomain truncation of the desmosomal cadherin, desmoglein 1: Implications for exfoliative toxin-mediated skin blistering.
Simpson CL, Kojima SI, Cooper-Whitehair V, Getsios S, Green KJ. American Journal of Pathology, 177(6):2921-37. DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.100397. PMID: 21075858
Abstract and Highlights
- Desmoglein 1 (Dsg1) is a desmosomal cadherin that is essential to epidermal integrity. In the blistering diseases bullous impetigo and staphylococcal scalded-skin syndrome, pathogenesis depends on cleavage of Dsg1 by a bacterial protease, exfoliative toxin A, which removes residues 1 to 381 of the Dsg1 ectodomain. However, the cellular responses to Dsg1 cleavage that precipitate keratinocyte separation to induce blister formation are unknown. Here, we show that ectodomain-deleted Dsg1 (Δ381-Dsg1) mimics the toxin-cleaved cadherin, disrupts desmosomes, and reduces the mechanical integrity of keratinocyte sheets. In addition, we demonstrate that truncated Dsg1 remains associated with its catenin partner, plakoglobin, and causes a reduction in the levels of endogenous desmosomal cadherins in a dose-dependent manner, leading us to hypothesize that plakoglobin sequestration by truncated Dsg1 destabilizes other cadherins. Accordingly, a triple-point mutant of the ectodomain-deleted cadherin, which is uncoupled from plakoglobin, does not impair adhesion, indicating that this interaction is essential to the pathogenic potential of truncated Dsg1. Moreover, we demonstrate that increasing plakoglobin levels rescues cadherin expression, desmosome organization, and functional adhesion in cells expressing Δ381-Dsg1 or treated with exfoliative toxin A. Finally, we report that histone deacetylase inhibition up-regulates desmosomal cadherins and prevents the loss of adhesion induced by Dsg1 truncation. These findings further our understanding of the mechanism of exfoliative toxin-induced pathology and suggest novel strategies to suppress blistering in bulbous impetigo and staphylococcal scalded-skin syndrome.